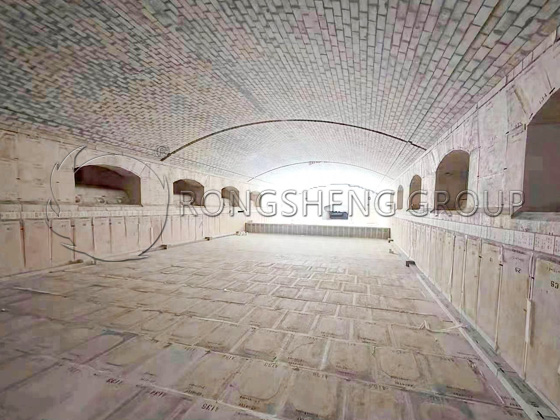
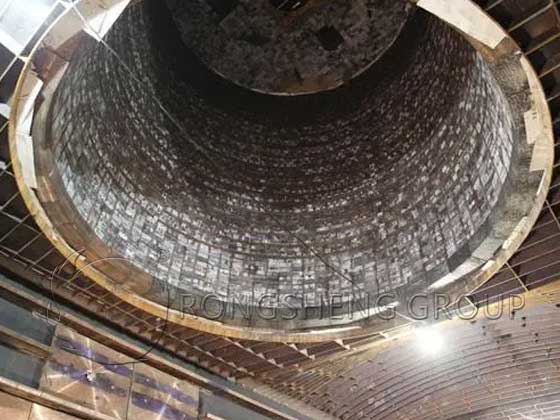
What are the performance requirements for electric furnace lining refractory materials? Electric furnace lining refers to the lining of the electric furnace smelting chamber, including the furnace cover, furnace wall, and furnace bottom parts. The quality of its work directly affects the quality of steel and other economic and technical indicators. Rongsheng Refractory Material Manufacturer specializes in providing refractory material services for high-temperature industrial furnaces. With rich experience in the production and sales of refractory materials, we can customize refractory lining materials according to the actual production conditions of the company. Product quality is reliable and customer service is guaranteed.

Performance Requirements for Electric Furnace Lining Refractory Materials
There are two types of refractory materials used in electric furnace linings: alkaline and acidic. At present, most electric furnaces use alkaline linings, and acidic lining electric furnaces are only used to produce steel castings or gray cast iron. There are several aspects to the performance requirements of electric furnace lining refractory materials.
- There should be sufficient fire resistance and load softening point. Because under the action of arc, the inner surface temperature of different parts of the furnace lining can reach 1500~1800℃.
- It should have strong slag resistance. Because slag and soot penetrate into the interior of the furnace lining through the pores at high temperatures. The refractory material is melted and delaminated, resulting in spalling.
- It should have good thermal shock resistance. Because during the steelmaking process, opening the furnace door, lifting the furnace cover, etc. will cause the temperature of the furnace lining refractory material to change suddenly. Flaking and chipping may occur, causing premature failure of the furnace lining.
- There should be sufficient strength. This is because the furnace lining is impacted during charging, vibrated during tilting, and washed away by metal, slag and airflow during boiling.
- The thermal conductivity should be small and the electrical conductivity should be low.
Commonly used refractory materials for electric furnaces include magnesia bricks, dolomite bricks, high alumina refractory bricks, siliceous refractory bricks, and magnesia cement. Since the working environment of each part of the electric furnace is different, the refractory materials used are also different.

Refractory Materials for Lining Calcium Carbide Furnaces
The performance of refractory materials used for lining calcium carbide furnaces requires high-temperature resistance and thermal shock resistance. The furnace cover, furnace door and furnace mouth of the calcium carbide furnace must be water-cooled. Therefore, in order to reduce the damage of high temperatures to refractory materials, we must choose refractory materials for lining.
The furnace door is an important part of the calcium carbide furnace. Traditional carbide furnace doors use corundum refractory bricks, corundum silicon carbide refractory bricks, silicon nitride bonded silicon carbide refractory bricks, corundum castables, etc. If you choose refractory bricks, they must be pre-laid and marked before they can be used for on-site construction. If corundum castable is used, the formwork can be constructed on site.
For traditional combined furnace door refractory bricks, the number of bricks used in the furnace ring is about 17 (two layers are required, and the mortar joints are staggered). At present, depending on the usage, the entire furnace door ring or three to seven bricks can be used for pre-laying. The reason is to resist the phenomenon of bricks falling off the furnace door. If the difference in size of the designed refractory bricks is too small, bricks will easily fall off. Therefore, try to make the difference between the big and small heads as large as possible to resist the phenomenon of brick falling.
The carbide furnace cover is made of low-cement refractory castables because water is passed inside for cooling. It should not leak air. The use of refractory castables can make the furnace cover airtight. The refractory castable used for the furnace cover must have good corrosion resistance, penetration resistance, strength, wear resistance and erosion resistance. Of course, the development trend of furnace covers using integrally cast prefabricated parts is also a good choice. Integral cast prefabrication not only has good air tightness, but also requires low-temperature sintering, which is also convenient for construction and has a long service life.
The furnace nozzle can be made of magnesium ramming material, which can not only protect the furnace nozzle, but also improve the safety of use. The furnace wall is made of first-class high alumina bricks, but the refractory bricks and fire mud must be made of phosphate refractory mud. Phosphate refractory mud has good bonding strength, small shrinkage at high temperatures, and strong slag resistance. The insulation layer of the furnace wall is made of lightweight clay refractory bricks or aluminum silicate fiber boards.
Carbon bricks are used for the bottom of the furnace, but the traditional small brick shape of 400*400 can no longer be chosen. Large bricks, 1200*1200, must be used. This staggered joint masonry reduces ash joints and extends the service life of the furnace bottom. For the lower part of the carbon bricks, 6-7 layers of clay refractory bricks or third-grade high-alumina refractory bricks are selected according to the furnace shape. The insulation layer uses lightweight clay refractory bricks or aluminum silicate fiber boards.
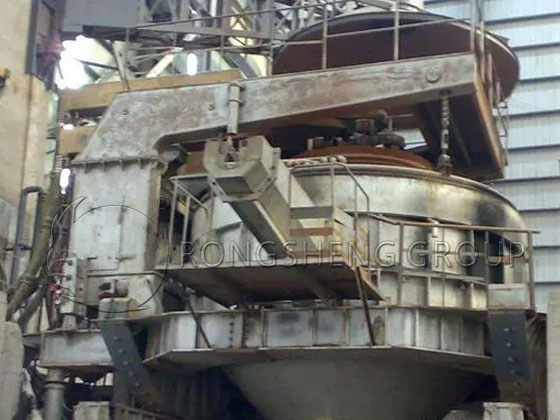

Refractory Materials for Insulating Electric Arc Furnace Linings
The insulation electric arc furnace uses electrode heating, and the inside of the furnace lining carries high-temperature slag liquid. When the high-temperature molten liquid comes out of the furnace, the temperature of the furnace wall will drop sharply. This causes the furnace lining refractory material to withstand the thermal shock of sudden cooling and sudden heating. It also has to withstand the chemical erosion of slag and the oxidative corrosion caused by contact with air during the drop of liquid level. Therefore, the requirements for the selection of furnace lining refractory materials are very strict.
At present, the refractory materials used for electric arc furnace linings mainly include magnesia-chromium spinel bricks, high alumina bricks, cold rammed paste and other refractory materials. However, these three refractory materials cannot meet the usage requirements during the production process. The service life does not exceed 3 months, resulting in the production line not being able to reach production capacity and being unable to meet production requirements.
The insulation electric arc furnace is lined with magnesia-chromium spinel bricks for the furnace walls and high-alumina bricks for the furnace bottom. After 10 days of production, the furnace wall was completely corroded and the furnace bottom was partially corroded. The furnace bottom was built with prebaked carbon bricks. After 10 days of production and use, the furnace wall was completely corroded and the furnace bottom was intact.
High-alumina bricks are used to build the furnace wall, and pre-baked carbon bricks are used to build the furnace bottom. This solution was produced and used for 40 days. The furnace wall was partially corroded, but the furnace bottom was intact. Cold ramming paste was used to build the furnace walls and prebaked carbon bricks were used to build the furnace bottom. After 30 days of production and use, the furnace walls were completely corroded and the furnace bottom was intact.
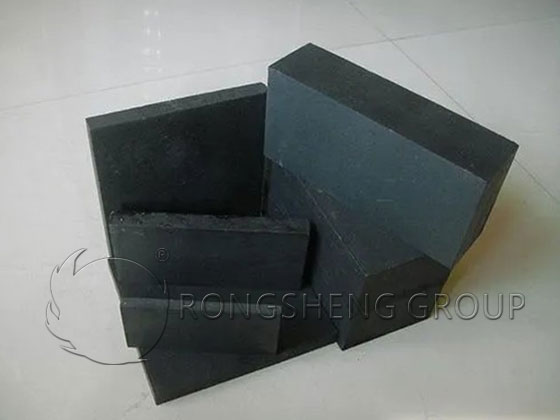

Prebaked carbon bricks are used to build the furnace walls and furnace bottom. After 90 days of production and use, the upper part of the furnace wall is fully oxidized and the furnace bottom is intact.
The hot slag of the insulation electric arc furnace is acidic slag. The furnace wall refractory materials have been washed away by acidic slag and have a very limited service life. The furnace bottom has a protective layer because the slag has not been poured out completely and the temperature is stable. It is feasible to use pre-baked carbon bricks to build the furnace bottom. Prebaked carbon bricks have high refractory resistance, excellent slag erosion resistance, excellent thermal conductivity and small expansion coefficient.
If silicon carbide nitride refractory products are used, they have corrosion resistance, resistance to molten cryolite wettability, oxidation resistance, wear resistance, high thermal conductivity, thermal shock resistance and extremely low electrical conductivity, and have a longer service life than other refractory materials. More than doubled. Silicon carbide nitride has good resistance to slag erosion. When used as the lining of the lower furnace body of an electric furnace, the structure does not change after high-temperature impact and contact with air, and its high-temperature resistance and anti-oxidation properties are excellent.
Since the price of nitrided silicon carbide material is too high, from a cost perspective, nitrided silicon carbide bricks and prebaked carbon bricks can be used together to build the lining of the insulation electric furnace. Prebaked carbon bricks are used for the furnace bottom masonry and the furnace wall inner masonry, and nitrided silicon carbide bricks are used for the furnace wall masonry for the outer masonry, which is in direct contact with hot slag and air. This mixed use prevents the prebaked carbon bricks from directly contacting the air, reduces the oxidation erosion of the prebaked carbon bricks, and reduces the cost of masonry. Moreover, the excellent performance of nitrided silicon carbide bricks can ensure the service life of the insulation furnace lining.