The thermal conductivity of silica bricks increases with increasing operating temperature without residual shrinkage. During the oven process, the volume of silica bricks increases as the temperature increases. During the oven process, the maximum expansion of silica brick occurs between 100 and 300°C, and the expansion before 300°C is about 70% to 75% of the total expansion. So, why does silica brick expand? Simply put, the expansion of silica brick is due to the expansion property of silica bricks. Specifically, the reason is that SiO2 has four crystal transformation points of 117°C, 163°C, 180~270°C and 573°C during the oven process. Among them, between 180 and 270°C, the volume expansion caused by cristobalite is large.

The thermal conductivity of silica bricks increases with increasing operating temperature without residual shrinkage. During the oven process, the volume of silica bricks increases as the temperature increases. During the oven process, the maximum expansion of silica bricks occurs between 100 and 300°C, and the expansion before 300°C is about 70% to 75% of the total expansion. So, why does silica brick expand? Simply put, the expansion of silica bricks is due to the expansion property of silica bricks. Specifically, the reason is that SiO2 has four crystal transformation points of 117°C, 163°C, 180~270°C and 573°C during the oven process. Among them, between 180 and 270°C, the volume expansion caused by cristobalite is large.
The expansion of silica brick comes from homogeneous polycrystalline transformation
SiO2 has seven variants and one amorphous variant under normal pressure. That is, β-quartz, α-quartz, γ-quartz, β-tridymite, α-tridymite, β-cristobalite, α-cristobalite and quartz glass. Transitions between the above variants can be divided into two categories:
The first type is the transformation between quartz, tridymite, and cristobalite. During the transformation, the original crystal structure must be destroyed (the Si-O bond is broken up) and a new structure must be reorganized. That is, the rearrangement of atoms is completed. Due to the large activation energy required, the transformation temperature is high and slow, accompanied by a large volume effect.
The second category is the transformation of the α, β, and γ types among the above-mentioned variants. Since they are very similar in structure and properties, the transformation is only a structural distortion and the Si-O bond is not dismantled. Therefore, the transformation occurs at a certain temperature, is a block, and is reversible. The time required to complete the transition between such variants is short-lived. At the transition temperature, the surface and surface of the crystal undergo an instantaneous transformation, and this variant can only coexist at the transition temperature.

Firing expansion of silica bricks
Silica bricks undergo phase changes during the firing process and have large volume changes. In addition, the amount of solution formed by bricks at the firing temperature is small (about 10%), making it much more difficult to fire than other refractory products. The firing system of silica bricks is related to a series of physical and chemical changes that occur during the firing process of the bricks, the quantity and nature of the added materials, the shape and size of the bricks, and the characteristics of the firing kiln.
- Physical and chemical changes of silica brick during the firing process. Silica bricks undergo the following changes in temperature sequence during the firing process. Drain residual moisture from bricks below 150°C. At 450°C, Ca(OH)2 begins to decompose. At 450~500℃, the dehydration of Ca(OH)2 is completed, the combination of silica particles and lime is destroyed, and the strength of the green body is greatly reduced. In the range of 550~650℃, β-quartz transforms into α-quartz. Since the transformation process is accompanied by a volume expansion of 0.82%, the quartz crystal will have microscopic cracks with varying densities. Between 600 and 700°C, the solid phase reaction between CaO and SiO2 begins, and the strength of the brick increases. Starting from 1100°C, the transformation speed of quartz increases greatly and the specific gravity of bricks also decreases significantly. At this time, the brick volume is greatly increased due to the transformation of quartz into a low specific gravity variant. Although the liquid phase is also increasing at this time, cracks can still occur in the range of 1100~1200.
- The volume of siliceous bricks changes during the heating process, which is different at different temperature stages. According to the changing characteristics of various types of silica green bodies, they can be divided into stages below 600℃, 600~1100℃, 1100~1250℃, and above 1250℃. There is a significant expansion in the β→α quartz transition between 500 and 600°C. At 700~800℃, there is a solid phase reaction between CaO and SiO2, which causes microscopic shrinkage. At 1000~1100℃, the shrinkage is more significant due to the formation of liquid phase. Starting from about 1200°C, the green body begins to expand violently due to the acceleration of quartz transformation.
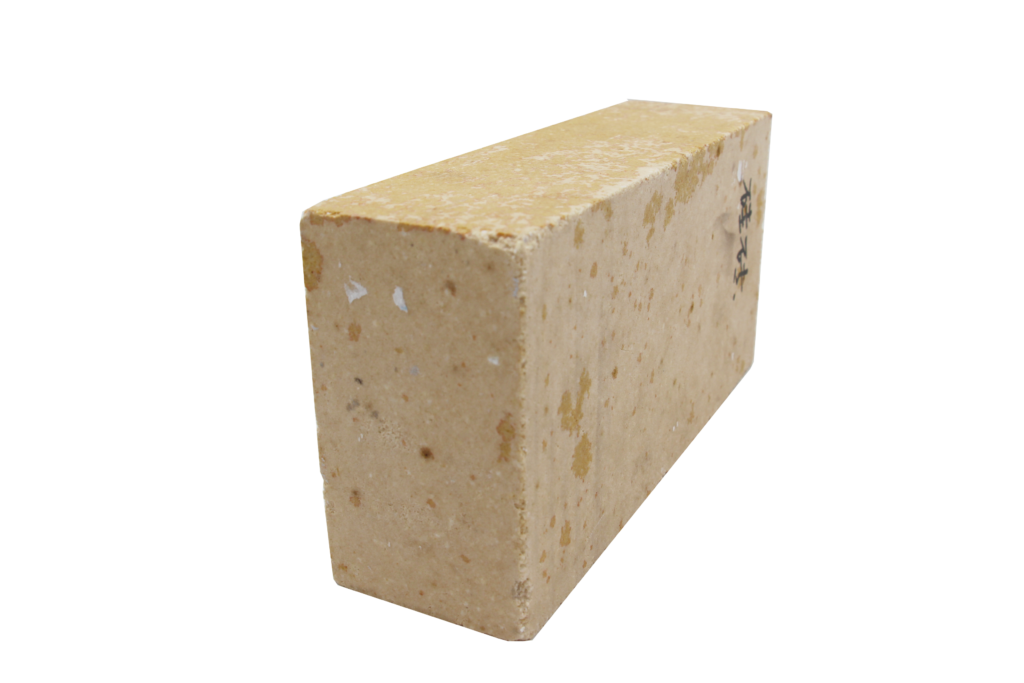

Silica Bricks Price in RS Refractory Materials Factory
Silica bricks are acidic refractory materials and are highly resistant to acidic slag erosion. However, when it is strongly corroded by alkaline slag, it is easily destroyed by oxides such as AI2O3 and has good resistance to oxides such as CaO, FeO, Fe2O3, etc.
When the working temperature is lower than 600~700℃, the volume of silica bricks changes greatly, the resistance to rapid cooling and rapid heating is poor, and the thermal stability is also poor. If the coke oven operates at this temperature for a long time, the masonry will be easily cracked and damaged.
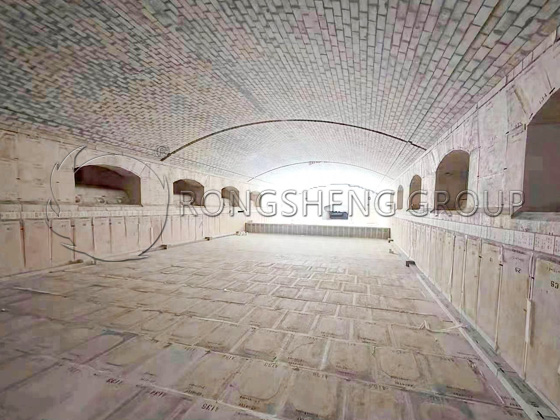
The silica bricks produced by RS Refractory Materials Factory are mainly used to build the partition walls of the carbonization chamber and combustion chamber of coke ovens, the roof and walls of glass tank kilns, and the firing kiln of silicate products. In order to increase production capacity, modern large coke ovens need to thin the walls of the coke oven’s carbonization chamber and combustion chamber, which requires the use of highly dense and high thermal conductivity silica bricks.
RS Refractory Materials Factory is located in Xinmi City, Henan Province. It is a company specializing in the production and operation of refractory products for external sales. We provide a comprehensive range of high-quality refractory services for high-temperature industrial kilns. If you need to buy silica brick and get silica bricks price, please choose a strong refractory brick manufacturer. The product quality is guaranteed, and there is perfect customer service to solve the after-sales problems of refractory lining materials.