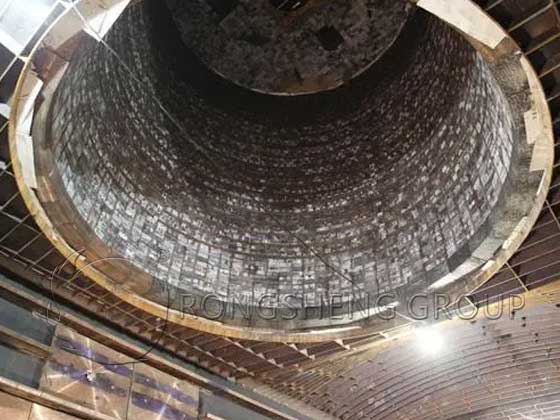
The life of the titanium slag electric furnace is one of the main factors affecting the production of titanium slag, especially because the production of titanium slag needs to complete the smelting process at a high temperature of 1600℃~1800℃. Since the titanium slag melt has extremely high chemical activity, it can react with almost all metal and non-metal materials. It can quickly corrode ordinary refractory materials, so it has high requirements for the physical and chemical indicators such as the material, refractoriness, and slag resistance of the titanium slag electric furnace lining. Magnesia Bricks for the slag zone. Improving the service life of the furnace body and reducing its cost is of great significance to the production of titanium slag.

At present, magnesia refractory bricks, high-alumina refractory bricks, and carbon refractory bricks are all used in titanium slag electric furnaces. The longest overhaul period of the titanium slag electric furnace body is 3 to 4 years, and the shortest is only half a year.
Factors Affecting the Service Life of the Furnace
Furnace lining material is a characteristic indicator of several refractory materials commonly used in titanium slag furnaces. Carbon bricks and graphite bricks have good refractory properties and will not bring in impurities. However, the activity of carbon increases at high temperatures and cannot withstand the effects of an oxidizing atmosphere, which accelerates the erosion of the furnace lining by titanium slag and molten iron in the furnace. At the same time, its price is relatively expensive. Magnesium bricks have a high refractoriness and their use temperature is close to the smelting temperature of titanium slag, so they are feasible for use in titanium slag electric furnaces. However, the MgO component in magnesium bricks will affect the quality of the titanium slag product. At the same time, the thermal expansion coefficient of magnesium bricks is very large. When the heating temperature exceeds its firing temperature of 1400℃~1650℃, residual shrinkage occurs. When the heating temperature reaches the titanium slag melting temperature of 1600℃~1800℃, the shrinkage phenomenon is very obvious, which is not good for masonry. The refractoriness of high-alumina bricks is slightly lower than the normal melting temperature of titanium slag. However, its use temperature is the same as that of magnesia bricks. It can also be used in titanium slag electric furnaces by treating the structure of the furnace body. The most important thing is that it is cheap and economical. In addition, high-performance corundum (AI2O3>95%) and zirconium oxide products are suitable for titanium slag electric furnace linings, but they are rarely used in titanium slag electric furnaces due to their high prices.
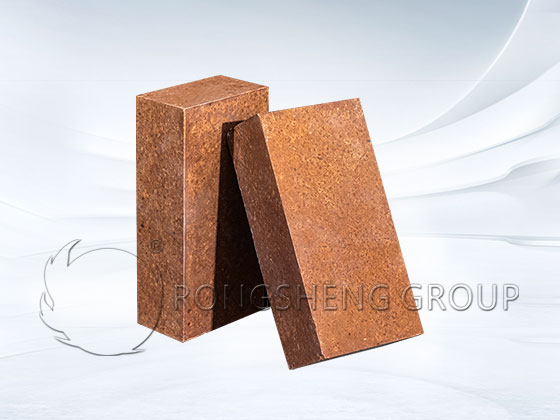

Furnace Lining Structure
Since the production of titanium slag electric furnaces is completed at high temperatures, the titanium slag melt is very corrosive. On the one hand, it can react with the refractory materials commonly used in metallurgy, and on the other hand, the slag and metal melt have a scouring effect on the furnace lining under high-temperature conditions. Therefore, the environment in which the smelting process is located is extremely complex and harsh. Therefore, a suitable furnace lining structure and sufficient working layer thickness are the premise and guarantee for extending the life of the furnace lining and realizing the normal production of the titanium slag electric furnace.
In addition to the heat from the molten pool, the heat in the furnace bottom of the titanium slag electric furnace also comes from the heat generated by the power consumption of the furnace bottom, so its temperature is relatively high, which is also one of the reasons why the furnace bottom is easily damaged. Therefore, the insulation measures of the furnace bottom will affect the service life of the furnace body. In production practice, a new 6300 kVA semi-closed titanium slag electric furnace in a certain factory was completed and put into production in April 2004. The construction and installation of the titanium slag electric furnace consumed 27 tons of refractory carbon bricks, 18 tons of high-alumina bricks, and 110 tons of clay bricks. If magnesia bricks are used as a furnace lining, about 93 tons of magnesia bricks and 100 tons of clay bricks are needed. Production effect: the titanium slag electric furnace has produced more than 1,400 furnaces since it was put into operation, and a total of about 6,000 tons of titanium slag has been produced.
Characteristics of Magnesia Bricks
Magnesia bricks can generally be divided into two categories: sintered magnesia bricks (also known as fired magnesia bricks) and chemically bonded magnesia bricks (also known as unfired magnesia bricks). Magnesia bricks with high purity and high firing temperature are called directly bonded magnesia bricks because the periclase grains are in direct contact. Bricks made of fused magnesia sand are called fused rebonded magnesia bricks. Alkaline refractory products with periclase as the main crystal phase have the characteristics of high-temperature mechanical strength, good slag resistance, strong corrosion resistance, and stable volume at high temperatures. Magnesia bricks have high refractoriness, good alkaline slag resistance, and high load softening start temperature, but poor thermal shock resistance. Sintered magnesia bricks are made of brick-making magnesia bricks. After crushing, batching, mixing, and molding, they are fired at a high temperature of 1550-1600℃. The firing temperature of high-purity products is above 1750℃. Unfired magnesia bricks are made by adding appropriate chemical binders to magnesia sand, mixing, molding, and drying. It is mainly used for steelmaking basic open hearth, electric furnace bottom, and wall, the permanent lining of oxygen converter, non-ferrous metal smelting furnace, high-temperature tunnel kiln, calcined magnesia brick and cement rotary kiln lining, heating furnace bottom and wall, glass kiln regenerator checker brick, etc.