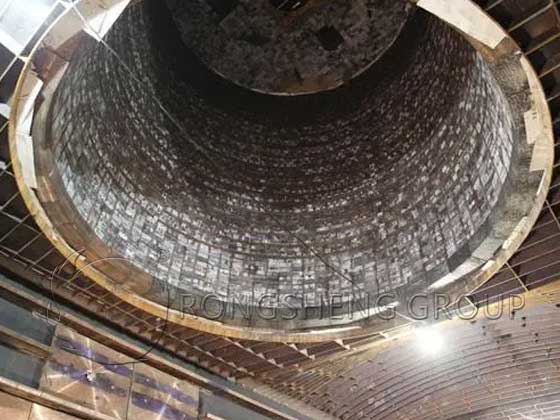
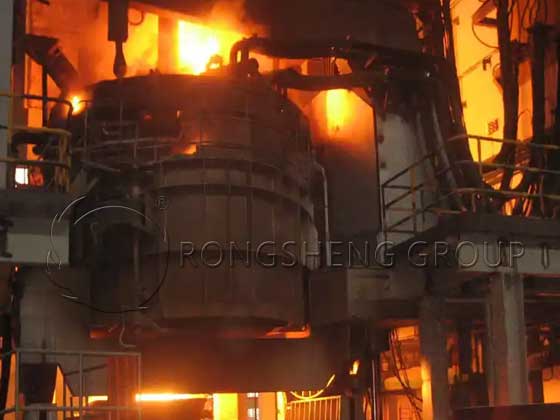
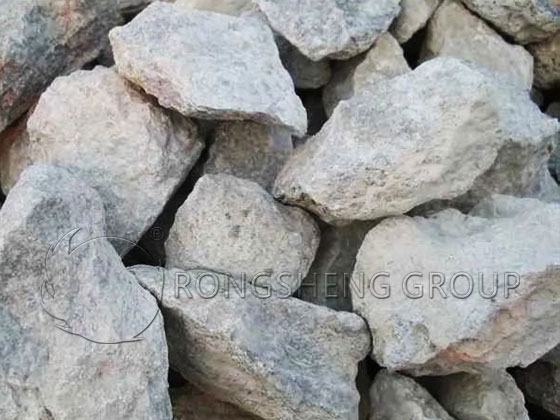
Magnesia-chrome bricks are refractory bricks made of high-purity magnesia, fused magnesia, and fused magnesia-chrome sand, which is formed by high pressure, dried, and fired at high temperature. The magnesia-chrome bricks produced by Rongsheng refractory materials manufacturer have low impurity content, high bulk density, good slag resistance, strong corrosion resistance, and high softening temperature under load. Magnesia-chrome bricks are widely used in metallurgical industrial furnaces, mainly used in non-ferrous metal smelting furnaces (copper, brazing, zinc, nickel, etc.) glass kilns, VOD, AOD, RH furnaces, electric arc furnaces, etc.

The Performance Characteristics of Magnesia Chrome Brick
Magnesia-chrome brick is an alkaline refractory material with a content of more than 85% magnesia and periclase as the main crystal phase. Magnesia chrome bricks are refractory bricks fired at high temperatures with fused magnesia and sintered magnesia. It is a refractory product with magnesium oxide and chromium trioxide as the main components, periclase, and spinel as the main mineral deposits, and magnesia-chrome bricks have excellent thermal stability. Magnesia-chrome brick is a kind of brick with high refractoriness and good alkali resistance slag function. The fired magnesia-chrome brick needs to be pulverized, batched, mixed, formed, and then fired at a high temperature of 1550 to 1600 °C. The firing temperature of high-purity products is above 1750℃.
Application of Magnesia Chrome Brick in Metallurgical Industry Furnace
Magnesia-chrome bricks are mainly used in the metallurgical industry, such as the construction of open hearth tops, electric furnace tops, out-of-furnace refining furnaces and various non-ferrous metal smelting furnaces. It is a high thermal erosion zone made of fused cast magnesia-chrome bricks and synthetic materials in the high erosion zone of the refining furnace outside the furnace. As well as magnesia-chrome bricks made of synthetic materials, high-erosion areas, and ultra-high energy consumption areas made of fused-cast magnesia-chrome bricks and synthetic materials. In addition, magnesia-chrome bricks can also be used in the firing zone of cement rotary kiln and glass kiln recuperation.

Application of magnesia chrome brick in converter
In the blowing of copper and nickel smelting, P-S converters are usually used. The P-S converter is a horizontal cylindrical converter. The lower part of the cylinder is provided with an exhaust hole for blowing air into the air or oxygen-enriched air. The iron sulfide in the nickel smelting furnace is simply removed, and it is only blown to form Ni3S2, which is only a stable compound at high smelting temperatures. Due to continuous blowing, Ni3S2 will be oxidized to NiO into the slag. The tuyere area is the easily damaged part of the copper converter. The main reasons are:
- (1) The working temperature of this part is relatively high, and the temperature fluctuates greatly. Before and after adding copper light, the time-varying rate of temperature reached more than 40℃/min.
- (2) Erosion, penetration of high-temperature melt, and scouring of gas and melt.
In the 1990s, the use of oxygen-enriched blowing technology made the use environment of refractory materials worse. Application of copper converter chrome brick in the copper converter. High-performance magnesia-chrome bricks have been widely used in the tuyere area of copper converters. Therefore, only by continuously improving magnesia-chrome bricks can we adapt to the development of converter smelting technology and improve the service life of converters.

Magnesia-chrome bricks and magnesia-chrome ramming materials for Isa smelting furnace
ISA smelting furnace is a vertical cylindrical furnace body, which is one of the important thermal equipment for non-ferrous metal smelting. The lining material of the Isa furnace is chromium magnesium refractory material. According to the actual working conditions, magnesia-chromium ramming material + high-alumina bricks are generally used for the bottom working lining of the Isa smelting furnace. The furnace wall adopts high-temperature resistance, erosion resistance, and good thermal conductivity directly combined with magnesia-chrome bricks or fused cast magnesia-chrome bricks. The magnesia-chrome bricks and magnesia-chrome ramming materials used in the ISA smelting furnace should follow the following specifications during the construction process.
- The masonry of each part should be wet-laid with staggered joints according to the design regulations.
- When the base layer of the furnace bottom is wet-laid with high-alumina bricks, expansion joints shall not be left. The gap between the high alumina brick and the furnace shell should be filled with refractory ramming material of corresponding material.
- Construction of magnesium-chromium ramming material. After the construction of the ramming layer is completed, it should be baked according to the oven curve.
- When the spare layer and the working layer are arc-shaped reverse arch furnace bottoms, 10mm100mm thick magnesia-chromium ramming material should be used between the two layers of reverse arch bricks to find the arc. The reverse arched bricks should be finely processed, and the upper part of the arched bricks should be level. The lowest point of the arc-shaped reverse arch bottom of the working layer should be at the same level as the emptying port.
- The upper and lower furnace walls of the slag should be built in a ring. The furnace wall should be built in sections after the bottom of the furnace is fixed with refractory bricks and the top of the reverse arch is leveled. There is a furnace wall with a water jacket structure in the molten pool area, and magnesia-chrome bricks should be built close to the water jacket. The upper elliptical cone furnace wall is masonry, and the setback should be uniform.
- The refractory packing between the spare layer and the working layer, the furnace wall, and the furnace shell should be tamped layer by layer, and the expansion joint should be reserved according to the design regulations. The expansion joint between the top of the furnace wall and the furnace top cover should be plugged with refractory ceramic fiber felt.
- Before the construction of the refractory castable for the furnace top cover, the surface of the heated steel member should be sprayed with high-temperature resistant paint. After the construction of the refractory castable plate of the furnace top cover, it should be maintained and installed according to the design regulations, and the gaps between the plates should be plugged with refractory ceramic fiber ropes.
- The weir mouth and safety discharge outlet should be pre-laid and should be carried out at the same time as the furnace body masonry, and no expansion joints should be left. The outer weir masonry should be built after the steel structure is installed.
The application of the Isa furnace in the non-ferrous metal smelting industry has strong advantages, it is easy to operate, has flexible control, and has low energy consumption. However, the life of the furnace body is short, and the refractory material is damaged quickly. Therefore, its construction and the selection of refractory materials are more important.

Rongsheng Refractory Manufacturer
Rongsheng refractory material manufacturer is a refractory material production and sales manufacturer with rich experience. Our technical team and our refractory products have served customers in more than 80 countries around the world. Examples, South Africa, Philippines, Chile, Malaysia, Indonesia, Vietnam, Kuwait, Turkey, Zambia, Peru, Mexico, Qatar, Egypt, Russia, Kazakhstan, etc. If you need to buy high-quality refractory products for metallurgical industry furnaces, magnesia-chromium bricks, or magnesia-chromium unshaped refractories, please contact us. Based on your specific needs, we will provide you with the most suitable refractory product for your production needs.